Changes compared to 23.6.1
23.6.1 ‘Voyager’ released
23.6.0 ‘Voyager’ released
Changes compared to 23.5.0
NOTICE: The "Run when PC Starts" option will now also apply to devices waking up from Sleep
New Features
- Protected Items defined by Policy can now optionally remain linked for future changes
- Added several new admin permissions to allow a global admin to help prevent a tenant admin from seeing the Comet service or storage provider types in use. The global admin can hide server history and server info widgets on the dashboard, prevent creation of storage via templates or custom storage, and can also filter the list of allowed cloud storage providers
23.5.0 ‘Thebe’ released
Thebe is the latest entry in our quarterly rollup series. It branches off from our main rolling Voyager development into a fixed target for our partners to qualify and build upon.
Like Comet's previous recent quarterly software releases, ‘Thebe’ is named after a moon of Jupiter, which in turn takes its name from an ancient Greek mythological figure. It is a very small moon with only 0.004x earth's gravity, meaning it is less likely to shape itself into a sphere - in fact a large impact crater covers around 40% of its surface area.
It was discovered by the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft in 1979, but owing to its small size and position, almost nothing more could be discovered until the next spacecraft Galileo visited two decades later. Scientists believe it contains water ice.
As for the software, Comet 23.5.0 ‘Thebe’ brings 10 features and 22 enhancements, including S3 Object Lock support for immutable protection against ransomware, a new design for the Comet Server web interface, an official Docker container, a C# SDK, support for Azure Key Vault codesigning, and more.
As always for a new quarterly release, there are two changelogs for 23.5.0 ‘Thebe’ depending on whether you are coming from the previous quarterly release or the previous Voyager release:
Changes compared to 23.2.2
Breaking Changes
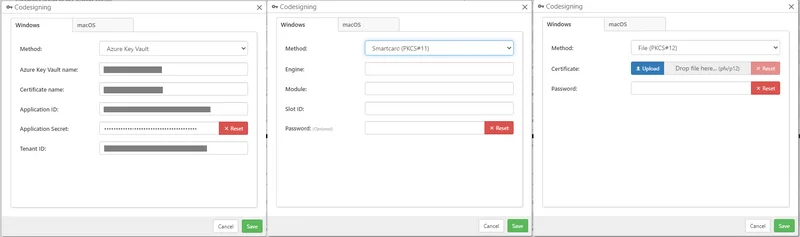
This release makes some changes to how codesigning works in Comet Server, which includes bundling a PKCS#11 engine.
- If you are using a hardware dongle for Authenticode EV codesigning, you may require an updated codesigning configuration
- Performing Windows codesigning from an ARM64 Linux version of Comet Server now requires glibc
New Features
- Cosmetic overhaul for the Comet Server web interface
- An official Comet Server docker container, which offers MSPs another deployment option. For more details, visit this link
- Support for Azure Key Vault as an option for Windows Authenticode codesigning
- Ability to use S3 object locking
- New option to permanently remove files marked for deletion in versioned S3 storage
- New Comet Server home page widgets for Protected Items types, server storage, server self-backup, and server replication
- When configuring an exclusion via Policy in the Comet Server web interface, default suggested exclusion paths have been added
- Ability to search for items to restore within Storage Vault snapshots via the Comet Server web interface
- A Test Connection button has been added to Storage Template configuration dialog
- Authenticode codesigning has been applied to the Comet Backup client uninstaller on Windows
23.3.9 'Voyager' released
Changes compared to 23.3.8
Bug Fixes
- Fix an issue with macOS devices failing to log in with an ERR_UNKNOWN_DEVICE error
- Fix an issue with the Recent Activity and Policies pages not loading correctly when hard-refreshed or loaded directly via URL
- Fix an issue with Comet default branding not presenting correctly following a server upgrade
23.3.8 ‘Voyager’ released
Changes compared to 23.3.7
New Features
- Release an official Comet Server docker container, offering MSPs another deployment option. For more details, visit: https://github.com/cometbackup/comet-server-docker
Enhancements
- Enhancement: Reduce peak memory usage when loading very large single files from a Storage Vault
- Enhancement: Reduce memory usage for S3-compatible Storage destinations
23.3.7 ‘Voyager’ released
Changes compared to 23.3.6
Enhancements
- Releasing a new version of Comet Client's internal Office 365 plugin. Users may see some changes in the way the Office 365 client behaves and what information is logged to the job details
- Allow top-level admins to create Tenant-assigned policies directly with the
AdminPoliciesNewAPI - Allow searching for device names in the quick search bar in the Comet Server web interface
- Add direct link to Bucket Users page from the Storage Role buckets page if Constellation is enabled
- Greatly expanded the internal event stream to include most events
- Added new event stream
FileOptionsthat allow users to log all events to file for audit or other purposes
23.3.6 ‘Voyager’ released
Changes compared to 23.3.5
Enhancements
- Enhancement: Significantly improve the performance of restoring files and folders from Disk Image Protected Items.
- Enhancement: Support application credential authentication for OpenStack Swift storage.
23.2.2 ‘Leda’ released
Changes compared to 23.2.1
Bug Fixes
- Fix an issue with Comet Server crashing if a Protected Item is owned by a non-existent device
- Fix an issue with deleting individual snapshots silently failing if the Storage Vault is currently being cleaned up by another device
- Fix a cosmetic issue with table page numbering in the Comet Server web interface if the language is set to Dutch
23.3.5 ‘Voyager’ released
Changes compared to 23.3.4
Enhancements
- Add Test Connection button to Storage Template configuration window
- Apply Authenticode codesigning to the Comet Backup client uninstaller on Windows
- Minor performance improvement when saving settings changes as a limited admin or tenant admin in the Comet Server web interface
Bug Fixes
- Fix an issue with Comet Server crashing if a Protected Item is owned by a non-existent device
- Fix an issue with searching of snapshots that could cause a crash in the Comet Backup desktop app
- Fix an issue with using the 'copy to clipboard' button when configuring Office 365 authentication from the Comet Server web interface on some web browsers
- Fix an issue with storage validation not working when configuring a Storage Template
- Fix an issue with incorrectly configured Backblaze Storage Vaults taking a long time to report an error
- Fix an issue with parsing the MFT for granular file restore if it is highly fragmented
- Fix a cosmetic issue with missing error text when failing to migrate a user account between tenants in the Comet Server web interface
- Fix a cosmetic issue with table page numbering in the Comet Server web interface if the language is set to Dutch
- Fix a cosmetic issue with some error popups saying 'message' instead of the real error message in the Comet Server web interface
- Fix a cosmetic issue with inconsistent field labeling for Azure Blob Storage between the Comet Backup desktop app and the Comet Server web interface
- Fix a cosmetic issue with some translated text not applying in the Comet Server web interface
- Fix a cosmetic issue with "Insert explanation here" help popups in the Policies section in the Comet Server web interface